I recently noticed that the hard disk on one of the Microsoft Windows Vista test systems that I use quite regularly began to fill up. This seemed odd to me because while I have a lot of data on the disk, the majority of it just test data (i.e. data that I copy over from my real system just so I have something to work with). I don’t really generate much, if any, data on that system. As such, I was a bit confused as to where all the disk space was going.
Using My Computer and a couple of third-party disk space analyzers just for good measure, I discovered that I could not reconcile the disk space usage. The system has a 120GB hard disk in it, and I could account for only about 80GB of data and installed applications. So why was the system displaying a low disk space warning message?
I immediately ran the Disk Cleanup tool and set about emptying and removing just about anything that could be using up disk space: the Recycle Bin, temporary Internet files, dump files, thumbnails, log files, temp files, error report files, and downloaded program files.
That seemed to help for a while, but the problem cropped up again.
After a bit more investigation, I discovered that the problem was being caused by a configuration problem with Vista’s System Restore feature.
In this edition of the Microsoft Windows Vista & Windows 7 Report, I’ll show you what I discovered and how you can fix it. As I do, I’ll also explain how to use the Volume Shadow Copy Service Administration command-line tool, VSSAdmin.
How System Restore works
Before we get started on the technique, let’s begin with a brief overview of how System Restore works.
System Restore is designed to take snapshots, called restore points, of your system state before certain types of operations, such as installing new drivers or installing Windows updates, are initiated. That way if a problem results from those types of operations, you can revert back to the restore point and essentially recover, or restore, your system to the state that it was in before the problem occurred.
These snapshots are taken by the Volume Shadow Copy Service. In addition to taking care of creating the restore points, the Volume Shadow Copy Service also monitors data files for the Previous Versions feature.
Using VSSAdmin
In order to manage the Volume Shadow Copy Service and ultimately System Restore, you’ll use the VSSAdmin command-line tool — there is no GUI tool in Vista for configuring System Restore. In order to run VSSAdmin, you must launch an elevated Command Prompt window.
To begin, right-click on the Command Prompt shortcut and select the Run as Administrator command. When you encounter the UAC, you will need to respond appropriately.
You can now use the VSSAdmin command-line tool to investigate and configure System Restore and the Shadow Copy Service. For example, you can obtain a list of all the restore points currently saved on the system by using the command:
vssadmin list shadows
You can see how much disk space is allocated to and used by System Restore and the Shadow Copy Service system by using the command:
vssadmin list shadowstorage
The investigation
On the Vista system that was running out of disk space, the result of the vssadmin list shadowstorage command is shown in Figure A. As you can see the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space settings was set to Unbounded, which means that there is no limit to the size it can grow and it was already at 40GB.
Figure A
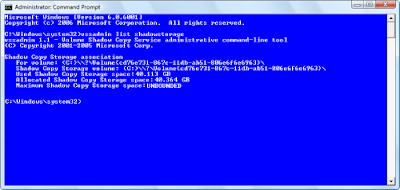 The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on the problem system was set to Unbounded.
The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on the problem system was set to Unbounded.
On another Vista test system, running on an 80MB hard disk, the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting was set to 11 GB, as shown in Figure B. This was a much more reasonable value. Why the value on one of my test systems was set to unbounded while the others had specific maximum values, I’m not sure.
Figure B


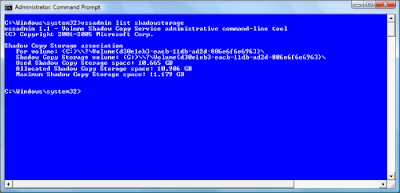 The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on another system was set to 11GB.
The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on another system was set to 11GB.
The solution
You can reset the value of the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting using the command:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for= /on= [/maxsize=
On my problem system, I reset the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting to 15GB using the command:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=c: /on=c: /maxsize=15GB
Once the operation was complete, I restarted the system, and everything has been running normally since.
Using My Computer and a couple of third-party disk space analyzers just for good measure, I discovered that I could not reconcile the disk space usage. The system has a 120GB hard disk in it, and I could account for only about 80GB of data and installed applications. So why was the system displaying a low disk space warning message?
I immediately ran the Disk Cleanup tool and set about emptying and removing just about anything that could be using up disk space: the Recycle Bin, temporary Internet files, dump files, thumbnails, log files, temp files, error report files, and downloaded program files.
That seemed to help for a while, but the problem cropped up again.
After a bit more investigation, I discovered that the problem was being caused by a configuration problem with Vista’s System Restore feature.
In this edition of the Microsoft Windows Vista & Windows 7 Report, I’ll show you what I discovered and how you can fix it. As I do, I’ll also explain how to use the Volume Shadow Copy Service Administration command-line tool, VSSAdmin.
How System Restore works
Before we get started on the technique, let’s begin with a brief overview of how System Restore works.
System Restore is designed to take snapshots, called restore points, of your system state before certain types of operations, such as installing new drivers or installing Windows updates, are initiated. That way if a problem results from those types of operations, you can revert back to the restore point and essentially recover, or restore, your system to the state that it was in before the problem occurred.
These snapshots are taken by the Volume Shadow Copy Service. In addition to taking care of creating the restore points, the Volume Shadow Copy Service also monitors data files for the Previous Versions feature.
Using VSSAdmin
In order to manage the Volume Shadow Copy Service and ultimately System Restore, you’ll use the VSSAdmin command-line tool — there is no GUI tool in Vista for configuring System Restore. In order to run VSSAdmin, you must launch an elevated Command Prompt window.
To begin, right-click on the Command Prompt shortcut and select the Run as Administrator command. When you encounter the UAC, you will need to respond appropriately.
You can now use the VSSAdmin command-line tool to investigate and configure System Restore and the Shadow Copy Service. For example, you can obtain a list of all the restore points currently saved on the system by using the command:
vssadmin list shadows
You can see how much disk space is allocated to and used by System Restore and the Shadow Copy Service system by using the command:
vssadmin list shadowstorage
The investigation
On the Vista system that was running out of disk space, the result of the vssadmin list shadowstorage command is shown in Figure A. As you can see the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space settings was set to Unbounded, which means that there is no limit to the size it can grow and it was already at 40GB.
Figure A
 The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on the problem system was set to Unbounded.
The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on the problem system was set to Unbounded.On another Vista test system, running on an 80MB hard disk, the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting was set to 11 GB, as shown in Figure B. This was a much more reasonable value. Why the value on one of my test systems was set to unbounded while the others had specific maximum values, I’m not sure.
Figure B


 The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on another system was set to 11GB.
The Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting on another system was set to 11GB.The solution
You can reset the value of the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting using the command:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=
On my problem system, I reset the Maximum Shadow Copy Storage space setting to 15GB using the command:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=c: /on=c: /maxsize=15GB
Once the operation was complete, I restarted the system, and everything has been running normally since.
No comments:
Post a Comment